Struggling with puffiness being attributed to water build up in the body and looking for how best to get rid of water weight in the belly without losing sleep? Read on!
The human body makes up to 60% of water and other fluid components whose functions are vital.
Sometimes, after some activities, there may be water retention in the Belly, which is usually uncomfortable.
This bloating may be mild or problematic, so you should eliminate it. Well, here’s how to.
There are many ways to get rid of belly water weight. Some methods include working out, a change in diet or even a drug prescription to reduce water retention in the stomach. The causes of bloating detail the day-to-day lifestyles of a person. Sometimes it can be troubling, but it is usually temporary. However, when the swelling isn’t reducing, you should seek medical attention immediately.
In this article, you’ll understand the reasons and causes of stomach bloating.
Additionally, we’ll discuss the ways and healthy maintenance lifestyle to avoid weight in the Belly.
How to Get Rid of Water Weight in the Belly
There are several ways to get rid of water retention in the Belly.
Exercise
Water is reduced during exercise because glycogen energy is used. According to research on movement and fluid retention, the number of fluid humans lose on average after an hour of activity ranges from 15 to 64 ounces (0.50-2 liters), depending on the environment and one’s clothing. Any physical activity that causes the body to sweat results in a rapid loss of water weight.
Drinking enough water after exercising is essential to replenish lost fluids and prevent dehydration. Your body moves a lot of water into the muscles while you work out. It aids in the reduction of extracellular water and the appearance of people who are carrying water weight. As a result, it’s common for people to shed a reasonable amount of body weight while exercising.
Increase Potassium Consumption

An essential electrolyte that plays a role in maintaining fluid equilibrium is potassium.
Boosting urine output helps counteract the effects of sodium and may help avoid fluid retention and water retention.
If you usually eat meals high in potassium, increasing your potassium intake may help you lose extra water weight.
Potassium is abundant in many fruits and vegetables, such as potatoes, apricots, spinach, and tomatoes.
Poultry, shellfish, dairy products, kidney beans, lentils, and other beans are excellent providers of potassium. Potassium can boost urine production and counterbalance sodium’s effects, which may prevent fluid retention.
Drink More Water
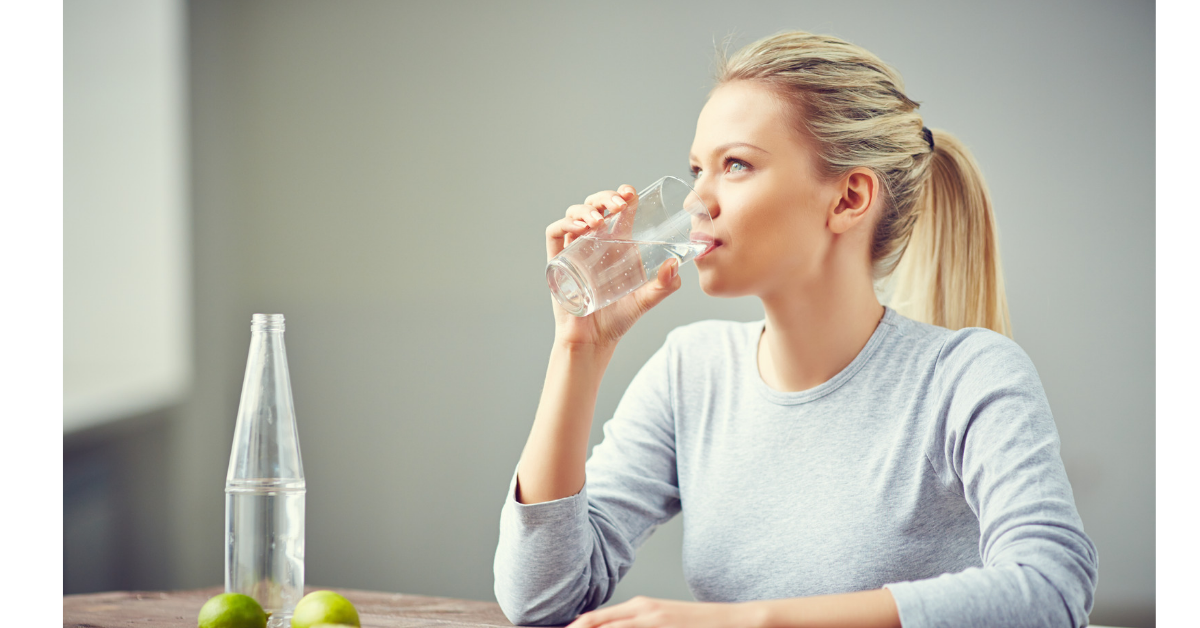

As they say, fight fire with fire. Drinking enough water sends a message to your body that it is not in danger of dehydration and can release additional water. Proper hydration is crucial for overall health.
The appropriate amount of water to consume depends on one’s lifestyle, level of physical activity, and geographic location, but maintaining proper hydration is crucial for the heart and general health.
Your overall water intake may also comprise other liquids and foods besides water. Include foods high in water content, such as cucumbers, romaine lettuce, celery, melons, and tomatoes, if you need help meeting your hydration objectives.
Reduction in Sodium

Salt or sodium overdose can quickly increase water retention. An essential electrolyte in the human body, sodium (salt), significantly impacts hydration levels. To function correctly, the body needs to maintain a balanced sodium-to-water ratio, but overeating salt makes you gain weight.
Although table salt contains a lot of sodium, processed foods—including practically anything packaged—comprise 75% of the sodium individuals ingest. We have them as cheese, soup bases, frozen dinners, pasta sauce, instant noodles, and salty snacks.
They are preserved and have an extended shelf life thanks to salt, and so do Natural foods with minimal salts, like vegetables, seeds, and nuts. So to lose water weight, the simplest thing a person can do is swap out high-sodium foods for these low-sodium ones.
Eat More Fiber Foods

Starting slowly will prevent your body from becoming overburdened if you don’t generally consume a lot of fiber. When fiber starts moving through your digestive tract, it will generate more gas but eventually help clear out the fermenting fecal matter lodged there.
Fiber makes you feel satisfied faster, which enables you to avoid overeating by signaling your body to drink more water. The healthy bacteria in your stomach are fed and encouraged by fiber, a prebiotic.
Supplements
Magnesium oxide and vitamin B-6 are two potent natural treatments for fluid retention. These supplements assist the kidneys in removing excess salt and water from the body. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms like water retention are also significantly reduced by them. They can also lessen leg edema and bloating in the abdomen.
How Long Does it Take to Reduce water in the Belly?
On average, A person can lose one to three pounds of water weight in two days. However, the precise timing and water weight loss depend on a person’s eating habits and activity level.
People lose water weight quickly when they alter their diet and maintain a rigorous daily exercise regimen. But, if your water retention results from a persistent health problem, the illness must often be treated before decreasing the water weight may be feasible.
Causes of the Water Weight in the Belly
Many things can cause water retention in the Belly. It could be temporary and unserious stomach bloating. However, there could also be severe health complications that may cause swelling in the stomach, hands, feet, ankles, and legs. The fundamental causes of water weight include:
Dehydration
Oddly, not drinking enough water causes water retention in the abdomen. Your body retains every drop of water when you don’t get enough to avoid being severely dehydrated. That also applies to alcohol.
As alcohol dehydrates you, it causes your body to store water even more, which results in unwelcome bloat the next day. On the plus side, quitting alcohol does at least have health advantages!
Menstruation
Another reason women can’t escape the water weight mayhem is presented here. Women’s hormones impact how well their kidneys work and how much fluid their bodies retain. Menstrual cycle modifications may affect water weight growth. This explains why you feel so bloated the week before your period and then deflate afterward.
Hormonal Changes
Water retention may occur during pregnancy or before a menstrual period due to changes in levels of certain hormones.
The rise in water retention in the body weeks before menstruation can be brought on by natural hormone changes. Moreover, during this time, cravings for carbohydrates and salty meals may cause more water retention in high-carb
Diets Choices
High sodium and high-carb diets can lead to water retention. In addition, potassium and magnesium deficiencies can also cause extra water weight.
Physical Inactivity
Sitting or standing for a long time stops fluids in the body from circulating properly. This causes water to build up around the body tissue, leading to swelling in the extremities.
Underlying Medical Issues
Some medical issues also contribute to weight retention in various body parts, including the Belly. Underlying medical problems like Kidney diseases, heart failure, lymphatic diseases, etc., have swelling, amongst other symptoms. These swellings can disrupt the normal blood flow around the body and retain fluids in parts of the body.
The disruptions can cause a buildup of fluids, resulting in swelling and extra water weight. Also, obesity may be associated with increased water retention in the core, arms, and legs. In addition, kwashiorkor, which is a protein deficiency, can cause water retention in the stomach.
Certain Medications
Water retention in the abdomen can be a side effect of various pharmaceuticals, including anti-inflammatory drugs, oral contraceptives, calcium-channel blockers, and some diabetic treatments. If your edema is small and you don’t have an underlying medical problem, you can reduce fluid retention with a few straightforward steps; several may indicate dangerous conditions that need medical attention.
Inflammation and swelling, typical components of your body’s immunological response, may be brought on by some infections. Therefore, patients should speak with their doctor whenever any drug has unsettling side effects.
Allergies
Histamine is a chemical released by your body when it recognizes an allergen; it causes fluid to seep from your capillaries into the surrounding tissues, resulting in temporary swelling and inflammation.
Is Water Weight in the Belly Something to be Worried About?
55 to 60 percent of an adult’s total body weight is typically made up of water. Therefore, water weight in the Belly is an additional amount of fluid the body has, which may cause discomfort and, possibly, temporal weight gain. In addition, bloating and puffiness can result from water retention in the Belly and arms and kegs.
A person’s weight can change by up to 5 pounds in a single day due to the dramatic change in water levels in the body. Significant water retention may be a sign of renal or cardiac problems. Most frequently, it is transient and disappears independently or after making a few easy lifestyle adjustments.
The body’s fluid balance fluctuates regularly, but when does it become urgent? Although water retention is a common problem, if edema occurs and persists, you should seek immediate medical assistance.
When the Belly suddenly begins to swell, especially while pregnant, you should be concerned since this could indicate the presence of a blood clot. Moreover, you should seek medical attention if you feel chest pain, shortness of breath, and edema.
If these symptoms get progressively worse and persist for more than a week with soreness and pains, they may be underlying conditions of Cancers of some abdominal or pelvic organs, heart failure, etc.
Is Water Weight in the Belly a Symptom of any Disease
The intricate parts of the body control the change in fluid levels. These organs responsible include the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular, hormonal, and urinary systems. As a result, the body might be unable to eliminate fluid as it should if any organs malfunction.
Capillary Damage
Capillaries are tiny blood arteries that control the body’s fluid balance. Some drugs, such as those prescribed for high blood pressure, might harm capillaries. Fluid is delivered to nearby tissues by capillaries. Cells receive nutrition and oxygen from this fluid, known as interstitial fluid.
The fluid then returns to the capillaries after dispensing the nutrients. Edema may develop if the capillaries are damaged. In addition, changes in capillary pressure and excessive capillary wallIs potential issues. If these issues arise, much liquid may leak from the veins and into the gaps between the cells.
The fluid will remain in the tissues, causing swelling and water retention, if the capillaries cannot reabsorb it. Systemic leaky capillary syndrome, an uncommon illness, causes this form of edema in specific individuals.
Congestive Heart Failure
The heart’s pumping motion aids in preserving proper blood vessel pressure. A person’s blood pressure will alter if their heart stops beating efficiently.
From this, fluid retention may result. As a result, there may be fluid in the lungs and swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles, which can cause a persistent cough or breathing problems. Congestive heart failure might eventually cause breathing difficulties and cardiac tension. As a result, it might be fatal.
The Lymphatic System
Across the body, lymph is transported by the lymphatic system. White blood cells are found in the fluid called lymph. It supports the immune system in protecting the body from infection. In addition, the lymphatic system assists the body in maintaining fluid balance by delivering and reabsorbing lymphatic fluid.
Fluid might accumulate around the tissues if the lymphatic system isn’t functioning correctly due to a malfunction. The abdomen, ankles, legs, and feet are just a few of the body regions that may expand due to this.
Kidney Failure
The kidneys filter the blood and support the body’s fluid balance. The kidneys’ tiny tubules serve as a filter for waste, liquids, and other substances.
The bloodstream absorbs anything the body can utilize again, and the kidneys can’t eliminate salt and fluid waste if they are not functioning correctly. Hence, the fluid will remain inside the body. For instance, lower limbs, hands, or the face may enlarge in people with chronic renal disease.
Pregnancy
The body retains more water than usual during pregnancy, which causes swelling in the lower limbs, particularly in warmer conditions or after prolonged standing. Other factors include hormonal changes and having additional abdominal weight.
Typically, this is not hazardous and usually goes away after delivery. But, if the swelling suddenly worsens, it could indicate pre-eclampsia.
This particular form of high blood pressure can be harmful to both the mother and the unborn child. Anyone who has headaches, nausea, discomfort in the ribs, vision issues, or significant edema when pregnant needs to consult a doctor right once.
Conclusion
In conclusion, water weight in the Belly can be temporary and with no adverse effect. Water retention in the Belly often results in various healthy lifestyles.
However, if specific symptoms persist, you must seek urgent medical help.
References:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320603
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/13-ways-to-lose-water-weight








